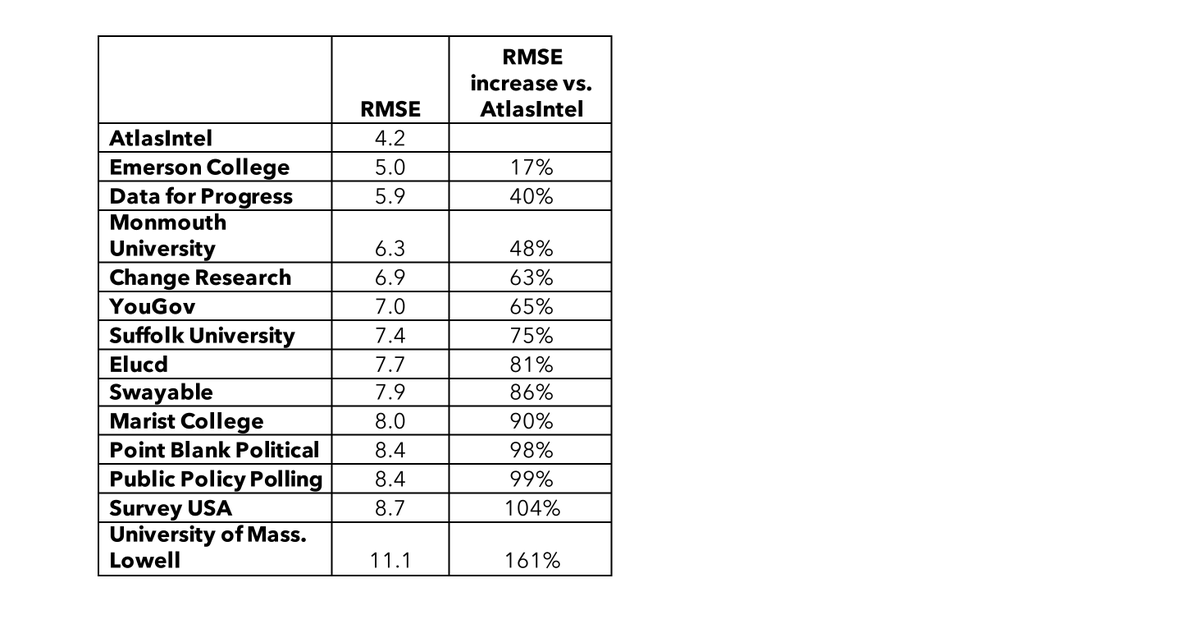
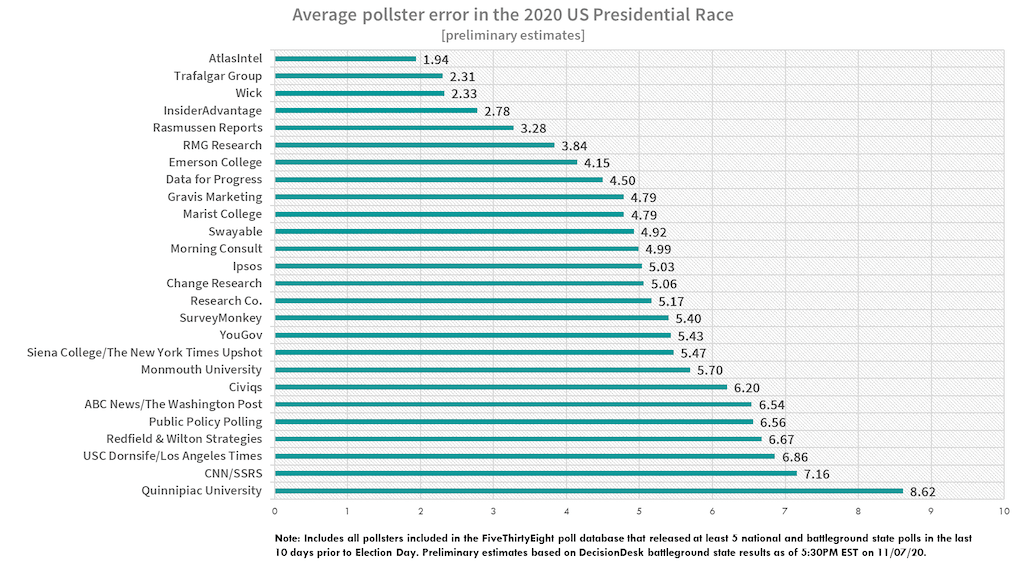
In today's data-driven world, understanding polling bias is crucial for making informed decisions. Atlas Intel, a leading authority in data analytics, has shed light on the complexities of polling bias and its implications. Polling bias can significantly skew results, leading to misinterpretations and incorrect conclusions. Whether it's political elections, market research, or public opinion surveys, recognizing and addressing polling bias is essential for accurate data analysis.
The term "polling bias" refers to systematic errors or inconsistencies that occur during the polling process. These errors can arise from various factors, including sampling methods, question wording, and respondent behavior. As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll discover how Atlas Intel approaches polling bias and provides solutions to minimize its impact. This article will explore the nuances of polling bias, offering insights and strategies to ensure reliable data collection and interpretation.
By understanding the mechanisms behind polling bias, individuals and organizations can better navigate the complexities of modern data analysis. Whether you're a researcher, marketer, or simply someone interested in understanding public opinion, this article will equip you with the knowledge to recognize and mitigate polling bias effectively. Let's explore how Atlas Intel is revolutionizing the way we interpret polling data.
Read also:Is Amc Popcorn Refillable
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Polling Bias
- Types of Polling Bias
- Atlas Intel's Approach to Polling Bias
- Sampling Methods and Their Impact
- The Importance of Question Wording
- Understanding Respondent Behavior
- Data Visualization Techniques
- Real-World Examples of Polling Bias
- Strategies to Mitigate Polling Bias
- Future Directions in Polling Analysis
Introduction to Polling Bias
Polling bias is a critical issue in modern data analysis, affecting the accuracy and reliability of polling results. It occurs when the sample or methodology used in a poll systematically favors certain outcomes over others. This bias can lead to misleading conclusions, impacting decision-making processes across various sectors. Understanding the root causes of polling bias is the first step toward addressing it effectively.
Atlas Intel Polling Bias research highlights several key areas where bias can occur, including sampling errors, non-response bias, and question framing. By identifying these issues, researchers can develop strategies to minimize their impact and ensure more accurate data collection. This section will explore the fundamental concepts of polling bias and its implications for data-driven decision-making.
Types of Polling Bias
Polling bias can manifest in various forms, each with its own unique challenges. Below are some of the most common types of polling bias:
- Sampling Bias: Occurs when the sample used in a poll does not accurately represent the population being studied.
- Non-Response Bias: Arises when certain groups are less likely to respond to a poll, leading to an unbalanced sample.
- Question Wording Bias: Happens when the phrasing of questions influences respondents' answers.
- Order Effect Bias: Results from the order in which questions are presented, potentially swaying respondents' opinions.
Each type of bias requires specific strategies to address, and recognizing these differences is essential for effective polling.
Atlas Intel's Approach to Polling Bias
Understanding Atlas Intel's Expertise
Atlas Intel is a pioneer in the field of data analytics, specializing in polling and survey research. With years of experience and a team of expert analysts, Atlas Intel has developed innovative methods to identify and mitigate polling bias. Their approach combines cutting-edge technology with traditional polling techniques, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
Atlas Intel's methodologies are grounded in rigorous scientific principles, emphasizing transparency and accountability in data collection. By leveraging advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms, they are able to detect and correct biases that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Read also:Silverado Resort And Spa Napa Valley California
Sampling Methods and Their Impact
Choosing the Right Sampling Technique
The choice of sampling method plays a crucial role in minimizing polling bias. Random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling are among the most commonly used techniques. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and selecting the appropriate one depends on the specific goals of the poll.
For example, random sampling ensures that every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected, reducing the likelihood of bias. However, it may not always be feasible or practical, especially for large or diverse populations. In such cases, stratified sampling can be more effective, as it divides the population into subgroups based on key characteristics and ensures proportional representation.
The Importance of Question Wording
Question wording is a critical factor in polling bias. Even minor changes in phrasing can significantly influence respondents' answers, leading to skewed results. To minimize this type of bias, pollsters must carefully craft questions that are clear, concise, and neutral.
Atlas Intel recommends avoiding leading or loaded questions, as these can subtly nudge respondents toward a particular answer. Additionally, using neutral language and providing balanced response options can help ensure that the data collected accurately reflects respondents' true opinions.
Understanding Respondent Behavior
Factors Influencing Respondent Responses
Respondent behavior is another important consideration in polling bias. Social desirability bias, for instance, occurs when respondents provide answers they believe are more socially acceptable, rather than their true opinions. This can be particularly problematic in sensitive or controversial topics.
Atlas Intel addresses respondent behavior by employing techniques such as anonymity and confidentiality, which encourage honest and open responses. They also use advanced algorithms to detect patterns of inconsistent or contradictory answers, helping to identify potential biases in the data.
Data Visualization Techniques
Presenting Data Clearly and Effectively
Data visualization plays a vital role in interpreting polling results. By presenting data in a clear and visually appealing manner, researchers can highlight key findings and trends while minimizing the impact of bias. Atlas Intel utilizes a range of visualization tools, including charts, graphs, and infographics, to communicate complex data in an accessible way.
Effective data visualization not only enhances understanding but also helps to identify potential biases that might otherwise be overlooked. By using consistent and transparent visualization methods, researchers can ensure that their findings are both accurate and reliable.
Real-World Examples of Polling Bias
Real-world examples of polling bias abound, providing valuable lessons for researchers and analysts. One notable example is the 2016 U.S. Presidential Election, where many polls underestimated support for Donald Trump. This discrepancy was largely attributed to sampling bias and non-response bias, as certain demographic groups were underrepresented in the polls.
Another example is the Brexit referendum, where polling errors led to widespread predictions of a "Remain" victory. In reality, the "Leave" campaign won, highlighting the importance of addressing polling bias in high-stakes situations. These examples underscore the need for rigorous polling methodologies and ongoing evaluation of potential biases.
Strategies to Mitigate Polling Bias
Best Practices for Accurate Polling
Mitigating polling bias requires a combination of best practices and innovative techniques. Below are some strategies that can help minimize bias in polling:
- Use random sampling techniques to ensure representative samples.
- Employ clear and neutral question wording to avoid leading respondents.
- Implement anonymity and confidentiality measures to encourage honest responses.
- Utilize advanced statistical models to detect and correct biases in the data.
- Regularly review and update polling methodologies to reflect changing circumstances.
By following these strategies, researchers can improve the accuracy and reliability of their polling results, ensuring that their findings are both meaningful and actionable.
Future Directions in Polling Analysis
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the field of polling analysis. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics offer exciting opportunities to refine polling methodologies and reduce bias. Atlas Intel is at the forefront of these developments, leveraging cutting-edge tools to enhance the accuracy and reliability of polling data.
Looking ahead, the future of polling analysis will likely involve greater integration of digital platforms, real-time data collection, and predictive modeling. These innovations promise to revolutionize the way we gather and interpret public opinion, providing more accurate insights than ever before.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing polling bias is essential for accurate data analysis and informed decision-making. Atlas Intel's research and methodologies provide valuable insights into the complexities of polling bias, offering practical solutions to minimize its impact. By recognizing the various types of bias and implementing best practices, researchers can ensure that their polling results are both reliable and actionable.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with polling bias in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into data analytics and polling techniques. Together, we can continue to advance the field of polling analysis and improve the way we interpret public opinion.